Anti-inflammatory foods can be viewed as foods that either prevent inflammation or reduce inflammation significantly. And this is connected to the immune system. When you have inflammation your body, you will experience pain in your body. This could be hip pain, shoulder or just arthritic pain. When this happens, relieving of the pain then becomes the focus.
The immune system gets activated when the body recognizes a foreign invasion, such as a plant’s pollen, microbe, or chemical. This process often triggers a process known as inflammation. However, sometimes inflammation may persist, even when you are not threatened by a foreign invader. Major diseases like arthritis, depression, cancer, heart disease, diabetes, and Alzheimer’s that plague us have been linked to chronic inflammation. Therefore, choosing the right anti-inflammatory foods will help to reduce the risk of illness, while consistently picking the wrong ones could speed up the inflammatory disease process.
An anti-inflammatory diet should include green leafy vegetables (kale, spinach, and collards), nuts (almonds and walnuts), olive oil, fatty fish (mackerel, tuna, salmon, and sardines), tomatoes, fruits (blueberries, cherries, strawberries, and oranges). Beverages and foods that reduce inflammation and chronic diseases are high in natural antioxidants and polyphenols, protective compounds found in plants.
In addition to reducing inflammation, unprocessed diet may also have some visible effects on physical and emotional health. Studies have highlighted nuts to be potent for the reduction of inflammation and lowering the risk of cardiovascular diseases and diabetes. Coffee may also help to combat inflammation because it contains polyphenols and other anti-inflammatory compounds. Eating healthy foods and diet will help to reduce the level of inflammation in the body. A diet or meal plan for anti-inflammatory food must consider a Mediterranean diet, which is high in nuts, fruits, vegetables, whole grains, fish, and healthy oils.
Before I jump in to talking about the specific foods that you can eat to help with inflammation, I think you should consider adding our in-house Better Joint Health Naturally. Our Better Joint Health Capsules together with the right kind of foods gives you’re the maximum protection that you need every single day. Click the image below to find out more.
These are some anti-inflammatory foods that you should try for the relief of pain;
1. Avocados: Avocados are rich in magnesium, potassium, fiber, and healthy monounsaturated fats. They also contain tocopherols and carotenoids, which are capable of reducing the risk of cancer. A compound in avocados may reduce inflammation in young skin cells. Avocados offer a lot of beneficial compounds that protect against inflammation and may reduce the risk of cancer. A study suggests that consuming a slice of avocado with a hamburger has lower levels of inflammatory markers NF-kB and IL-6, as compared with those who ate the hamburger alone.
2. Peppers: Chili peppers and Bell peppers are very rich in vitamin C and antioxidants with powerful anti-inflammatory effects. Chili peppers contain ferulic acid and sinapic acid, which may lower inflammation and promote healthier aging. Bell peppers produce quercetin, an antioxidant that may reduce one marker of oxidative damage in people with an inflammatory disease known as sarcoidosis. Chili peppers and bell peppers are rich in sinapic acid, quercetin, ferulic acid, and other antioxidants with strong anti-inflammatory effects. Capsaicin is derived from hot chili peppers. Typically, topical capsaicin may be very effective in relieving pain. It works by depleting substance P, a compound that conveys pain sensation from the peripheral to the central nervous system. This takes some days for this to happen.
3. Mushrooms: Mushrooms contain phenols and other antioxidants that provide anti-inflammatory protection. They are low in calories and rich in selenium, copper, and all of the B vitamins. Though various varieties of mushrooms exist globally, only a few are edible and grown for commercial purposes. These include the portobello mushrooms, truffles, and shiitake.
Lion’s Mane, a special type of mushroom may potentially reduce low-grade and obesity-related inflammation. However, a study found that cooking mushrooms significantly lowers their anti-inflammatory compounds. Therefore, it could be best to eat them lightly cooked, or raw. Some edible mushrooms have compounds that may lower inflammation. Eating them raw or lightly cooked may help you benefit from their full anti-inflammatory potentials.
4. Berries: Berries contain antioxidants called anthocyanins, and these compounds have anti-inflammatory effects that may reduce inflammation, boost immunity, and reduce the risk of heart disease. The body produces natural killer cells, which help the immune system to function properly. Berries consist of small fruits that are highly rich in vitamins, fiber, and minerals. Though varieties of berries exist, some of the most common berries are raspberries, blackberries, blueberries, and strawberries. A study about men showed that those who consumed blueberries every day produced significantly more NK cells than those who did not. In another study, it was noted that adults with excess weight who eats strawberries have lower levels of certain inflammatory markers associated with heart disease.
5. Green tea: Green tea is one of the healthiest beverages in the world. It reduces the risk of Alzheimer’s disease, obesity, heart disease, cancer, and other conditions. Myriad of green tea’s benefits are pegged on its antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties, especially a substance called epigallocatechin-3-gallate (EGCG). Studies have shown that EGCG inhibits inflammation by reducing the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines and damages the fatty acids in your cells. Therefore, Green tea’s high EGCG content helps to lower inflammation and safeguard cells from damages that can lead to diseases.
6. Fatty fish: Fatty fish are known as a great source of protein, and the long chain of omega-3 fatty acids (EPA and DHA). Although all types of fish contain some omega-3 fatty acids, these fatty fish, such as sardines, herring, mackerel, salmon, and anchovies are among the best sources.EPA and DHA reduce inflammation that can lead to heart diseases, metabolic diseases, diabetes, and kidney diseases. The body metabolizes these fatty acids into compounds called protectins and resolvins, which have anti-inflammatory effects.
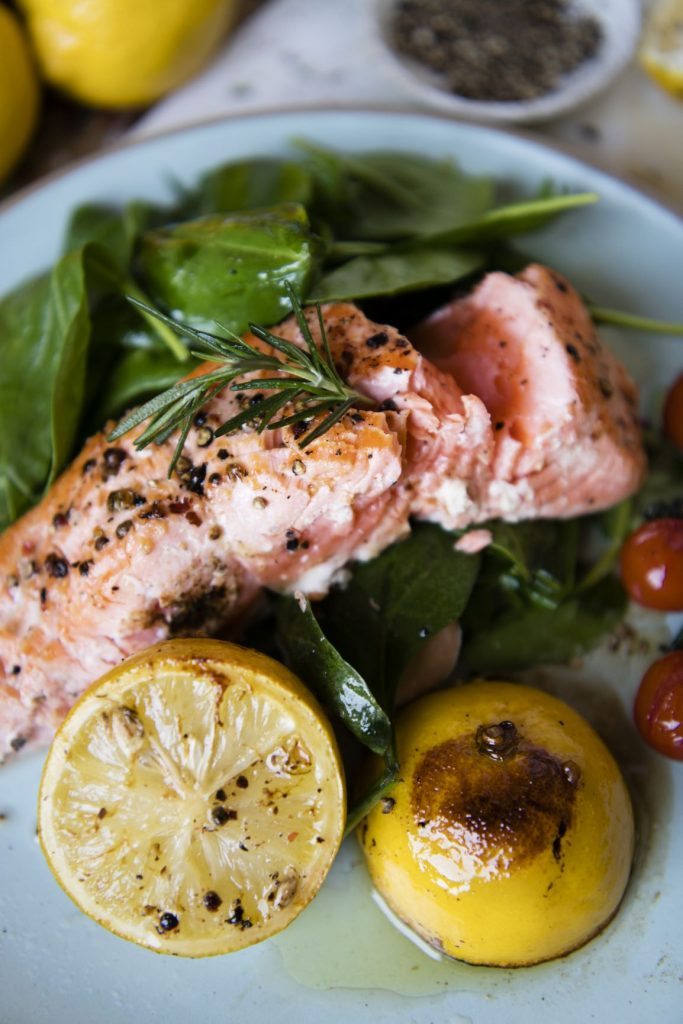
Several studies have found out that people who consume salmon or EPA and DHA supplements tend to experience a reduction in the inflammatory marker C-reactive protein (CRP). However, in another study, those with an irregular heartbeat who consumed EPA and DHA daily experienced no difference in inflammatory markers, when compared with those who received a placebo. Fatty fish have high amounts of omega-3 fatty acids, EPA and DHA, and these compounds have anti-inflammatory effects.
7. Broccoli: Broccoli boast of sulforaphane, an antioxidant that combats inflammation by lowering the levels of cytokines and NF-kB, which triggers inflammation. Broccoli is extremely nutritious, and one of the major sources of sulforaphane, an antioxidant with powerful anti-inflammatory effects. Broccoli is a healthy vegetable, alongside Brussels sprouts, cauliflower, and kale. Studies have shown that eating a lot of nutritious vegetables is linked with a reduction in the risk of heart disease and cancer. This may be as a result of the anti-inflammatory effects of the antioxidants that Broccoli contains.
8. Grapes: Grapes equally have anthocyanins, which reduce and combats inflammation. In addition to lowering inflammation, they may reduce the risk of several diseases, such as diabetes, obesity, heart disease, Alzheimer’s, and eye disorders. Grapes are also one of the best and major sources of resveratrol, another compound that has many health benefits. A study highlighted that people with heart disease who consumes grape extract daily tend to experience a reduction in inflammatory gene markers, including NF-kB, and an increase in their level of adiponectin. A reduction in levels of adiponectin is associated with weight gain and an increase in the risk of cancer. Several plant compounds in grapes, such as resveratrol, can reduce inflammation, and may also reduce the risk of several diseases.

9. Turmeric: Turmeric is a widely sought-after spice with a strong and earthy flavor that is mostly used in curries and Indian dishes. Tumeric has become sought-after for containing Curcumin, a powerful anti-inflammatory nutrient. Turmeric lowers inflammation related to diabetes, arthritis, and other diseases. A study noted that consuming 1gram of curcumin daily combined with piperine from black pepper triggers a significant decrease in the inflammatory marker CRP in people with metabolic syndrome. However, it may be difficult to get enough curcumin from the only turmeric to be able to experience a visible effect. In another study, women with excess weight who took 2.8 grams of turmeric per day were found to have shown no improvement in inflammatory markers. Therefore, taking supplements that contains isolated Curcumin is more effective.
Eating black pepper with turmeric can significantly boost the absorption of curcumin. Curcumin supplements are often combined with piperine, which can improve curcumin absorption by two thousand percent (2,000%). Turmeric is a spice that has been used to relieve arthritis pain and heartburn, and to reduce inflammation for ages. There are a lot of studies trying to figure out how turmeric works against pain or inflammation, but its ability to reduce pain and inflammation may be due to a chemical called curcumin, which has anti-inflammatory properties. Turmeric is usually safe to use, but high doses or long-term use may cause indigestion. People with gallbladder disease should avoid using turmeric.
10. Extra virgin olive oil:

Extra virgin olive oil is rich in mono-unsaturated fats and a staple in the Mediterranean diet, which provides numerous health benefits. It is one of the healthiest fats to eat. Studies have associated extra virgin olive oil with a reduction in the risk of brain cancer, heart disease, and other serious health conditions. In a study on the Mediterranean diet, CRP and several other inflammatory markers significantly lowered in those who consumed 1.7 ounces (50 ml) of olive oil daily. Extra virgin olive oil offers greater anti-inflammatory benefits than those provided by more refined olive oils. The effect of Oleocanthal, an antioxidant found in olive oil, has been compared to anti-inflammatory drugs like ibuprofen. Extra virgin olive oil provides powerful anti-inflammatory benefits, which may lead to a reduction in the risk of heart disease, cancer, and other serious health conditions.
11. Dark chocolate and cocoa: Dark chocolate is packed with antioxidants that reduce inflammation. They are delicious, rich, and satisfying, and may also reduce the risk of disease and foster healthier aging. Flavanols are responsible for chocolate’s anti-inflammatory effects and keep the endothelial cells that line your arteries healthy. According to a study, smokers experience significant improvements in endothelial function within 2 hours of eating high-flavonol chocolate. Flavanols in dark chocolate and cocoa can reduce inflammation. They may also reduce your risk of several diseases. However, make sure to choose dark chocolate that contains at least 70% of cocoa (a greater percentage is even better) to be able to experience its anti-inflammatory benefits.
12. Tomatoes: Tomatoes are highly rich in potassium, vitamin C, and lycopene, an antioxidant with impressive anti-inflammatory properties. Lycopene may be particularly beneficial in reducing inflammatory compounds related to several types of cancer. Tomato is unarguably a nutritional powerhouse, and an excellent source of lycopene, which may reduce inflammation and protect against cancer. A study showed that drinking tomato juice significantly decreases inflammatory markers in women with excess weight, but not those with obesity. Cooking tomatoes with olive oil can increase the amount of lycopene you absorb, and that’s because lycopene is a carotenoid; a nutrient that is better absorbed with a source of fat.
13. Cherries: Cherries are delicious and rich in antioxidants, such as catechins and anthocyanins, which help to combat and reduce inflammation. Though the health-promoting properties of tart cherries have been studied more than other varieties of cherries, sweet cherries equally provide health benefits. According to a study, when people consume 280 grams of cherries per day for a month, their levels of the inflammatory marker CRP decreases and stays low for 28 days after they stopped eating cherries. Factually, Sweet and tart cherries contain antioxidants that reduce inflammation and the risk of diseases.
14. Bromelain:

Pineapples are tasty tropical fruits that could help with muscle and joint pain because of Bromelain, an enzyme found in pineapple juice and pineapple stem. This enzyme is often used to reduce inflammation and prevent muscle soreness after intense exercise, it is also believed to be effective for hayfever sufferers. Bromelain is a proteolytic enzyme that assists the body’s digestive system in breaking down complex protein molecules. Studies have found Bromelain to be effective in relieving symptoms of sinus and acute nasal inflammation when combined with other medications.
15. Black pepper: This spice is loaded with anti-inflammatory agents. The unique flavor of black pepper comes from the chemical, piperine. Piperine, even at low doses has been shown to reduce inflammation, inhibit the spread of cancer, and crush the perception of pain and arthritis symptoms.
16. Cinnamon: Cinnamon acts as an anti-inflammatory agent, and its antioxidant properties can lessen the risk of cellular damage and chronic diseases. Cinnamon blocks growth associated with abnormal cell growth, therefore protecting the body against cancer. Cinnamon is a spice that is used for toast and lattes, and also could be used as an effective antioxidant in foods. For thousands of years, extracts from the bark as of the cinnamon tree, including the leaves, fruits, flowers, and roots have also been used in traditional medicine globally.

Cinnamon helps to heal the skin and clear away scars and acne from the skin because of its antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties. Procyanidins and Catechins, are two powerful antioxidants found in the bark of Cinnamon. In a study carried out on rats, Procyanidins and Catechins were found to accelerate the anagen (an active growth stage of hair follicles) phase of hair growth. Cinnamon was also discovered to have the highest antioxidant activity in a study involving 26 spices. This spice ranks high on the oxygen radical absorbance capacity scale.
In another study, cinnamon water extract was discovered to have anti-inflammatory properties, and this could be as a result of it containing polyphenol. Cinnamaldehyde, a compound found in cinnamon was said to have the potency to inhibit the production of nitric oxide. This compound, cinnamaldehyde, found in Cinnamon is very effective for healing wounds due to its antimicrobial and anti-inflammatory properties.
Cinnamon is speculated to have a potential effect on a sore throat and oral health. Its antibacterial properties make it effective for treating oral infections, and other toothaches. It may also help to eradicate halitosis or bad breath.
Essential oil gotten from the bark of Cinnamon was found to have some anti-inflammatory effects, so it is used in many countries for the treatment of inflammation and other skin conditions. The relaxing and relieving effects of cinnamon essential oil make it effective for aromatherapy. An oil extracted from cinnamon, Eugenol, is adopted by a lot of dentists as a local anesthetic. This spice is used for multi medicinal purposes, and richly grown in Sri Lanka, Indonesia, India, and other Asian countries.
CONCLUSION
Have plans on how to manage pain before and after surgery, this will help you to be mentally prepared for what’s to come. Avoid foods that are capable of muscle inflammation. In addition to stocking your diet with nutritious and anti-inflammatory recipes, it’s essential to reduce your consumption of foods that are capable of causing inflammation. Below are some of the foods that have been linked to increased levels of inflammation:
- Refined carbohydrates, such as flour tortillas, pasta, white rice, white bread, crackers, and biscuits.
- Fried foods, such as donuts, fried chicken, French fries, egg rolls, and mozzarella sticks.
- Junk foods, such as convenience meals, potato chips, pretzels, and fast food.
- Processed meats, such as salami, hot dogs, smoked meat, bacon, beef jerky, and canned meat.
- Sugar-sweetened beverages, such as energy drinks, sports drinks, soda, and sweet tea.
- Trans fats, such as margarine, shortening, partially hydrogenated vegetable oil.
Highly processed, overly greasy, or super sweet food isn’t ideal if you have inflammation. Inflammation sometimes occurs naturally, as part of the body’s immune response. When the body is fighting an infection or injury, it sends inflammatory cells to the rescue, and this results in symptoms such as redness, swelling, and sometimes pain. Chronic inflammation occurs when the body is always in a state of high alert, this can trigger certain major health issues like Alzheimer’s disease, heart disease, diabetes, and cancer.
Inflammation levels are somewhat within control, but factors like smoking, overweight or obesity, or drinking excessively can increase the risk of inflammation. Diet also plays a role in triggering or lowering inflammation, and studies have shown that switching the foods and drinks you consume could be very helpful in reducing inflammation levels than depending on prescription drugs. Taking prescription or over-the-counter drugs for chronic or severe pain, only when it is necessary is also idealistic, as various medications have discomforting side effects, such as drowsiness, dizziness, seizure, and loss of memory.
Low levels of inflammation continuously may trigger various diseases. Consuming a wide variety of delicious and antioxidant-rich foods will reduce the risk of inflammation. When experiencing a condition that leads to inflammation, it is beneficial to change diet and consume more anti-inflammatory foods. Anti-inflammatory food includes fruits and vegetables, plant-based proteins, fatty fish, whole grains, and fresh herbs and spices. Studies have shown that leafy greens, such as spinach and kale, that are in vitamin K helps to lower inflammation, and so do broccoli and cabbage.
Whole grains, such as brown rice, whole-wheat bread, Oatmeal, and other unrefined grains tend to be high in fiber, and fiber may also help to reduce inflammation. Beans are high in fiber, rich in antioxidants and other anti-inflammatory substances. Nuts have a healthy kind of fat that helps to prevent inflammation. However, take a handful of nuts per day, lest the fat and calories level may accelerate. Fish are known to help in lowering inflammation. Studies have shown that omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids are some of the most effective natural anti-inflammatory agents available on earth. The discovery of vascular inflammation being the prime cause of coronary artery disease has made fish and fish oil supplements highly recommended for the prevention of this disease by the American Heart Association.

Another study has shown that countries with the highest fish consumption have a lower incidence of neurodegenerative disease and depression. The biological tenets for the effectiveness of fish oil in treating arthritis have been properly documented after many positive clinical studies and constant comparison to traditional pharmaceutical anti-inflammatory agents. In a study carried out recently, 250 patients with cervical and lumbar disc disease, who were taking nonsteroid anti-inflammatory drugs, revealed that fifty-nine percent (59%) of nonsteroid anti-inflammatory drugs could be replaced with fish oil supplements as a natural anti-inflammatory agent. The standardized dosage is a total of 1.5–5g of EPA and DHA, taken with meals daily.


