Relief for knee pain shouldn’t be so difficult for anyone with such a problem. Having knee pain is common and usually not a sign of something serious—many possible causes, ranging from a simple muscle strain or tendonitis to some form of arthritis. Sometimes a cause cannot be known. Pain in the knee can often be treated at home with our very own Better Joint Health Naturally with CBD Supplements, and you should start feeling better after a few days. As we age, knee pain can become more common. Weighty people are also at a greater risk of having knee pain. Knee pain can sometimes be the result of a sport or another injury.
To understand just how good our Better Joint Health Naturally with CBD Supplements are and they can help relieve the pain in your knees, let’s talk a little bit about your knee and its structure.
Structure of the knee in the human body
Experts revealed that the knee is the largest joint in your body. It is made up of four main elements: bones, ligaments, cartilage, and tendons.
Bone
The knee joint is formed where three bones meet. These are:
- the femur, also known as the thighbone
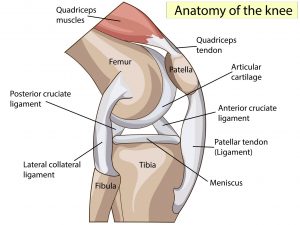
- shin, also known as the tibia
- the Kneecap, which is also known as a kneecap.
Ligaments
These join bones to other bones. There are four main ligaments in the knee. They act like strong ropes to bind the bones together and hold the knee in place.
These knee ligaments are:
- Collateral ligaments: These are located on the sides of the knee. One is in, and one is out. They control the lateral movement of the knee.
- Cruciate ligaments, which are located inside the knee joint. They cross to form an X. These ligaments control the way the knee moves back and forth.
Cartilage
The two types of cartilage in the knee are:
- Articular cartilage
This covers the ends of the femur and tibia and the back of the patella. It is a slippery substance that helps the knee bones glide smoothly against each other as you straighten or curve your leg.
- Meniscal cartilage
This is also known as a meniscus. They are two wedge-shaped pieces that act as shock absorbers between the shin and the femur. The medial meniscus is located on the deeper and inner side of the knee joint. The lateral meniscus is located on the outer side of the knee. The meniscus helps cushion and stabilize the joint, making them durable and elastic. Whenever people say they have a torn cartilage in the knee, they are usually talking about a torn meniscus.
Could my knee pain be arthritis?
Knee pain can develop gradually over time, can come on suddenly, or can come and go repeatedly. Whatever the pain pattern, if it is not due to arthritis, it can be in some people.
Osteoarthritis is the most familiar type of arthritis. Arthritis can affect anyone at any age but is more common in people over 50. If you are suffering from acute osteoarthritis of the knee, you may sometimes experience knee pain and stiffness. It can affect one knee or both. The pain may worsen at the end of the day or when you move your knee and get better when you rest. You may get a little stiff in the morning, but it usually doesn’t last more than half an hour.
Osteoarthritis pain can be felt around the knee or only in a particular place, such as the front or side. You may feel worse after moving your knee in a specific way, such as walking up or downstairs.
Causes of Knee Pain
Research has proven that osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis, sprains, and gout are among the most common causes of knee pain.
Osteoarthritis
According to NHS UK, Osteoarthritis is a condition that causes joints to become painful and stiff. One of the most prevalent causes of long-term knee pain. One common reason for long-term knee pain is a type of arthritis known as osteoarthritis. It is believed to be caused by wear and tear on the joint. It mainly affects people over the age of 70. The knee bends and straightens smoothly due to the cartilage covering the bones’ ends in the healthy joint. Very long damage to this cartilage leads to osteoarthritis. Movement is limited, and the pain gradually increases. Pain worsens with weight-bearing and eases with rest. Pain also appears after waking up or after periods without moving. Movement reduces stiffness.
Rheumatoid arthritis
Another type of arthritis, rheumatoid arthritis (RA), can also cause knee pain. Rheumatoid arthritis happens to involve swelling of the knee. Sore joints will be red, tender, hot, and swollen. The pain involves a more general stiffness that is usually worse early in the morning. There may be fatigue in the afternoon. Knee pain with these symptoms requires a doctor’s attention for proper diagnosis and treatment. Rheumatoid arthritis reduces from early treatment.
Sprains, strains, and injuries
Sprains and strains occur when the knee’s tissues are stretched by an unusual or increased activity, twisting, or awkward stumbling.
Gout
This is another type of arthritis. It causes sudden episodes of severe knee pain with redness and swelling and can affect other joints. The condition can be treated with medical treatment with medications and changes in diet and exercise.
Knee Pain Remedies
Knee pain is the most typical condition that could be caused by both short-term and long-term problems. Many short-term knee problems do not require the help of doctors, and often people can help them to recover. Home remedies can also be of help with a lot of the long-term problems related to knee pain.
12 home remedies to relieve knee pain
Remedy for knee pain will depend, sometimes, on the origin and cause of the ailment. Below are simple treatments that can help with many forms of knee pain.
- Physical activity
Exercise can slow down the growth of osteoarthritis (OA), one of the most common causes of knee pain. Healthcare professionals urge people to exercise to control knee OA. Walking, cycling, swimming, tai chi, and yoga can all be helpful. Physical activity improves the health of cartilage tissue, whether or not a person has OA. Exercise also energizes the way the body supports the joints. Strengthening the leg muscles is especially helpful for the knees. People with joint pain can benefit from aqua aerobics activities, which puts little pressure on the knees.
- Strengthening exercises
People can book a session with a physical therapist to identify the best exercises and programs for their needs. Strengthening the muscles of the upper leg, the quadriceps muscles, through exercise, can help protect the knee joint. These muscles are located on the sides and the front side of the thighs.
Below are some ways to strengthen these muscles:
- Stretch and raise one leg while lying down or sitting.
- Put one foot on a step, then the other, go back down, and repeat the steps.
- Sit in a chair and then get up and repeatedly sit for one minute. Try this in a gentle and controlled manner and avoid using your hands for support.
- Hold onto a chair and squat down until the kneecaps cover the toes. Do it ten times.
- Posture and support
Measures that can help minimize knee stress include:
- avoiding low chairs and sofas where you “sink.”
- sit on a cushion to raise the seat level if necessary
- check that you have good sitting posture, without bending or bending over
- wear supportive shoes and avoid those with broken arches, as these can cause abnormal force and wear on the knee
- Avoid sitting for a long time and spending a lot of time without moving, as joints can become stiff and painful without moving.
- Weight loss and diet
People who are weighty or obese are at a higher risk of knee pain. Carrying extra weight puts more work on your joints. Losing it helps reduce long-term knee pain, including pain caused by arthritis. The extra weight on your body increases inflammation throughout your body, and your knees are affected. Eating well helps you maintain weight. A healthy diet means a balanced diet that is:
- rich in fruits, vegetables, and fiber
- low in meat, animal fats, and other fats
Experts at the Arthritis Foundation recommends a Mediterranean-style diet full of fresh produce. Experts also urge people with osteoarthritis of the knee to lose weight if they are overweight or obese. A dietitian or medical doctor can help decide how much weight a person should lose. They can also help you plan an excellent and proper diet.
- Medicines

Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs and other medicines can help with knee pain that is caused by arthritis. Many of these anti-inflammatory drugs need to be administered in a doctor’s office, but others can be used at home, with or without a prescription. Medicines that can help control pain include:
- tramadol
- Acetaminophen and duloxetine, which is an antidepressant, can help.
- topical capsaicin
- steroid injections into the joint
- Oral or topical non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs)
Experts advise against the use of opioids, except tramadol. Some of these drugs are available for purchase without a prescription or online, including the NSAIDs ibuprofen and naproxen.
- Massage
Massage, including self-massage, can relieve knee pain. Experts recommend the following.
- These should be done in a sitting position with your knees forward and your feet flat on the floor.
- Slightly clenching your hands into fists, strike the upper, lower, and middle thigh ten times with both hands. Repeat three times.
- Sitting with your feet flat on the floor, place the palm of your hand on your thigh and slide it down to your knee, then release. Repeat five times. Repeat it with the inside and outside parts of the thigh, too.
- Insert four fingers into the knee tissue and move it up and down five times. Repeat around the knee.
- Place the palm of your hand on the upper thigh, slide it along the thigh, above the knee, and back on the outer part of the thigh.
- Gently massaging the thigh muscles will have a beneficial effect on the knee and another part of the leg.
Current guidelines: We do not recommend intense massage as a treatment for osteoarthritis of the knee, as there is not enough evidence to show that it helps reduce symptoms. However, massage can offer other benefits, such as stress management.
- Aromatherapy preparations
In-depth research suggested that massage with an oil containing ginger and orange improves pain and function in the knees with moderate to severe pain due to osteoarthritis. In the research, the researchers found that applying an ointment containing cinnamon, ginger, mastic, and sesame oil had a similar effect on pain, stiffness, and movement as if using salicylate ointment.
- Protection, rest, ice, compression, and elevation (PRICE)
Rest, ice, compression, protection, and elevation can help cure mild knee pain of a soft tissue twist or tear.
Protection refers to shielding the knee from further injury by breaking from the action that made it happen.
Rest can help reduce the risk of any further injury and give the tissues time to heal. However, stopping all movements is not recommended, as this can lead to stiffness and, over time, muscle weakness and pain.
Ice can help relieve swelling and inflammation. It should be encased in a cloth and applied for twenty minutes several times on the first day of the injury. Avoid placing ice straight on the skin, as this can cause more damage.
Compression with knee support, for example, can increase comfort levels. The backing or bandage should be firm but not tight.
Elevating or keeping your leg elevated will stimulate circulation and reduce swelling. Ideally, the knee should be raised above the level of the heart.
- Hot and cold
Hot and cold can help treat low back pain and have been recommended for relieving joint pain resulting from arthritis. Heat relaxes muscles and improves lubrication, reducing stiffness. Use a hot water bottle or hot sanitary napkin. Ice encased in a cloth can relieve severe pain, acute inflammation, and also swelling.
- Climate
Colder weather is often thought to make the pain worse. The results of the study do not support this, although living in a pleasant climate could facilitate pain psychologically. It can also provide easier opportunities for a healthier lifestyle. Researchers found that, rather than the weather itself, sensitivity to climate in older people with osteoarthritis can affect how they experience joint pain. Southern European people, women, and people with higher anxiety levels were more likely to report sensitivity to weather conditions. Higher sensitivity levels were more likely to report increased pain, especially in weather wet or rainy and cold. The study results do not support the common belief that pain is worse in cold weather. Scientists conducted in the United States supported this view. The results showed no link between the rains and increased visits to the doctor for pain in the joint.
- Acupuncture
A few years back, a study involving five hundred and seventy people found evidence that acupuncture could help people with knee osteoarthritis. Participants received 23 proper acupuncture sessions or 23 shams for 26 weeks, or six acupuncture sessions for 12 weeks. Those who had real acupuncture scored higher in pain and function than the others. The ACR and AF point out that acupuncture can help relieve pain and strain.
- Apple cider vinegar and many other meals
According to various sources, apple cider vinegar (ACV) has anti-inflammatory properties that relieve arthritis and other pain types. Nevertheless, there is no concrete scientific evidence to support this. The Arthritis Foundation calls stroke a “food myth.”
Other popular arthritis tips include:
- Be careful to consume collagen, gelatin or pectin and raw foods.
- Avoid dairy products, acidic foods, and vegetables, like tomatoes, eggplant, and potatoes.
There is no solid and concrete proof to show that these are helpful or can even be recommended.
Pain in The Front of The Knee
Strain and pain in the front of the knee are some of the most common discomforts. It is second only to low back pain – about a quarter of people will suffer from it at some point in their life. It commonly affects teenagers, especially young athletes. It is the most popular overuse syndrome in athletes. Most cases of anterior knee pain are overuse injuries or poor exercise preparation. Pains and distress usually go away on their own, and sports activities can be resumed after the pain has passed. Pain varies but tends to:
- produce weakness in the legs
- being a dull ache that begins gradually and is activity related
- click sounds or other sounds
- lights up when walking upstairs or standing up after sitting, bending over, or kneeling for a long time
Recommended Treatments for Anterior Knee Pain Include:
- Staying away from the activities that trigger it until it is resolved
- apply ice when your knee hurts
- administering over-the-counter painkillers like ibuprofen or naproxen
- applying strengthening exercises and activities
When to see a doctor
An apparent knee injury caused by sudden trauma, such as a car accident or a fall, may require immediate medical attention. A doctor should check a knee if there is significant pain, deep cuts, swelling, or if the person is unable to use the leg properly. For the rest cases of knee pain, a doctor will need to investigate the problem if:
- persists for a long time
- progressively worsens
- interrupts daily activities
It is essential to obtain a diagnosis and treatment from a doctor if knee pain involves red, sore, hot, and swollen joints. If the symptoms are persistent, involving other joints, and other morning stiffness symptoms, it could be rheumatoid arthritis. Doctors can administer medications for the disease and the pain it also causes.
When a swollen knee is very hot and painful, and there are other general symptoms of discomfort, this is the time to seek urgent medical help. The knee could be infected, and severe infection can be dangerous. This requires urgent hospital care. Anyone who gets medical help from knee pain should see their doctor again if the problems worsen or if there are any problems with treatment, such as a side effect of a drug. Anyone with knee pain who is receiving medical care should see their doctor again if problems get worse or if there are any problems with treatment, such as a side effect of the medicine.
Knee exercises
Staying active and indulging in exercise is an essential part of treatment and will aid recovery speedily. Being physically fit while recovering from knee pain can:
- prevent pain from coming back
- helps maintain your current fitness level, even if you make changes to the way you do things, any activity is better than none
- Keep other muscles and joints strong and flexible.
It is essential to keep the muscles around the knee healthy, as this will take the strain off the knee region. These muscles include the hip muscles, thigh, and calf.
Knee stretch exercises
Try doing these exercises every day.
- Straight Leg Raise (Seated)

Sit with good posture in a chair. Straighten one leg, hold and slowly count to 10, then slowly lower the leg. Repeat ten times with each leg. Do your best to get into the habit of doing this exercise every time you sit down.
- Muscle stretching
Lie on your back with a rolled towel under the ankle of the affected leg. Bend the other leg at the knee. Use your straight leg muscles to push the end of the knee firmly onto the bed or floor. Hold the position for a gentle count of five. Do your best to repeat at least five times with each leg. This exercise helps prevent permanent knee flexion. Try doing this at least once a day when you are laying on the ground.
- Leg stretches
Sit on the floor and stretch out your hand in front of you. Slowly bend one knee toward your chest, sliding your foot across the floor, until you feel a slight stretch. Hold the position for five seconds. Straighten your leg as much as possible and hold this position for five seconds.
Repeat ten times with each leg. If you cannot get down to the floor, sit on a sofa and use a table or tea tray as a surface to slide your foot.
For help with your knee, you should order your Better Joint Health Naturally with CBD Capsules and we will ship them to you ASAP!

